Getting to grips with all the podcasting jargon can be tough when you start a new podcast. For anyone wondering what bit depth is or scratching their head when asked if the recording is in mono or stereo, this guide has you covered. Saspod's Podcast Glossary is your podcasting resources guide to help you on your podcasting journey!
Podcast Glossary: Podcasting
Podcast words about podcasting is a bit of a tongue-twister. In this section, you'll find all podcast phrases related to the creative side of podcasting.
Audiocast
Audiocast is a word for any audio file that is available for online download. This could include a podcast, radio show, streamed content, or other online audio resources.
Metadata
Metadata is the technical term for the essential information about your podcast that you give to podcast platforms when you fill out your RSS feed. It includes your show title, publisher, description, episode title, episode notes, and category.
Monetization
Monetization in podcasting refers to generating income through your podcast. Podcast monetization can be created through live tours, selling merch, crowdfunding, advertising, sponsorship, fan donations, and publishing platform payments.
Hosting
When your podcast is published, a podcast hosting site will distribute it to listening platforms. At Saspod, we provide this service to clients to make it easier for their episodes to go live. The podcasting hosting service acts like a home for your podcast; the host then distributes it to platforms like Amazon Music, Apple Podcasts, or Spotify.
Content Creator
A content creator produces entertaining or educational content for distribution across online platforms. Content creators often post on Instagram, Facebook, and blogs to engage with their audiences. Often, content creators host podcasts to promote their brand and expand their audience.
Podcast Guest
A podcast guest is a valuable person in the podcasting world. When they appear on the show to take part in an interview, podcast guests create valuable content. Many podcast guests host their own podcast shows, which opens promotional opportunities for the host. In return, the guest is expected to have the host on their show.
Podcast Host
The podcast host is the creator of the show. The host leads the way, asking questions, discussing their topics of expertise, and engaging with their audience. It's the host's job to be the "face" of the podcast; they conceptualize the show, create the brand, and ensure their podcast succeeds.
Podcast Co-host
The podcast co-host is a great role that involves supporting the host. A co-host is expected to provide commentary, ask questions to keep the conversation going, and offer a few good laughs when needed. Co-hosts can also take on responsibilities like researching and writing questions to help the host prepare.
Category
A podcast category refers to the genre of your podcast. When creating the metadata for your show, you'll need to provide a category. Some examples of categories are health and wellbeing, finance, food and drink, comedy, true crime, and more. Choosing the right category is essential for your SEO and reaching your target audience.
Episodes
When you publish your show, you'll need to know how to label it. Podcasts are recorded in episodes so that you can number and name them accordingly.
Show Notes
Podcast show notes are a written description of your podcast episode. Show notes summarize the episode so the viewer can know what it is about before listening to it. Show notes can also include information like the guest's contact information, links to products mentioned in the episode, or other relevant information.
Timestamps
Timestamps are used to identify topic points throughout the podcast episode. It helps the listener navigate to topics they're interested in or lets them know the part to return to if they want to hear about a specific topic again.
Podcast Glossary: Equipment

A podcast glossary wouldn't be complete without a list of podcast equipment. This section lists every piece of tech you need to record a podcast.
Condenser Microphone
A condenser microphone is a type of podcast microphone that provides outstanding audio recording quality. Because of its sensitivity to sound, it's an excellent choice for podcasting. Check out our guide: What is a condenser microphone?
Phantom Power
Condenser microphones have an active electronic circuit and require power to work. Phantom power sends direct current to the condenser microphone and creates a phantom circuit to power it. Phantom power source supplies are usually built into mixing consoles and pre-amps, so they're easy to operate.
Dynamic Microphones
A dynamic microphone is a durable and budget-friendly podcast microphone, so if you're starting out, this is the mic for you. Dynamic mics convert sound to electrical signals using electromagnetism. They're great for louder environments, so if you're hosting a lively podcast, it'll be a great fit. Check out our guide: What is a dynamic microphone?
USB Microphone
USB microphones are popular among podcasters and streamers because they're so easy to use. Recently, Blue Yeti took the USB mic world by storm with its state-of-the-art USB mic. USB mics can be plugged directly into your PC and work seamlessly with all recording software. It's a great option if you don't want to spend money on a full audio system or don't have the time for a complicated setup.
Polar Patterns
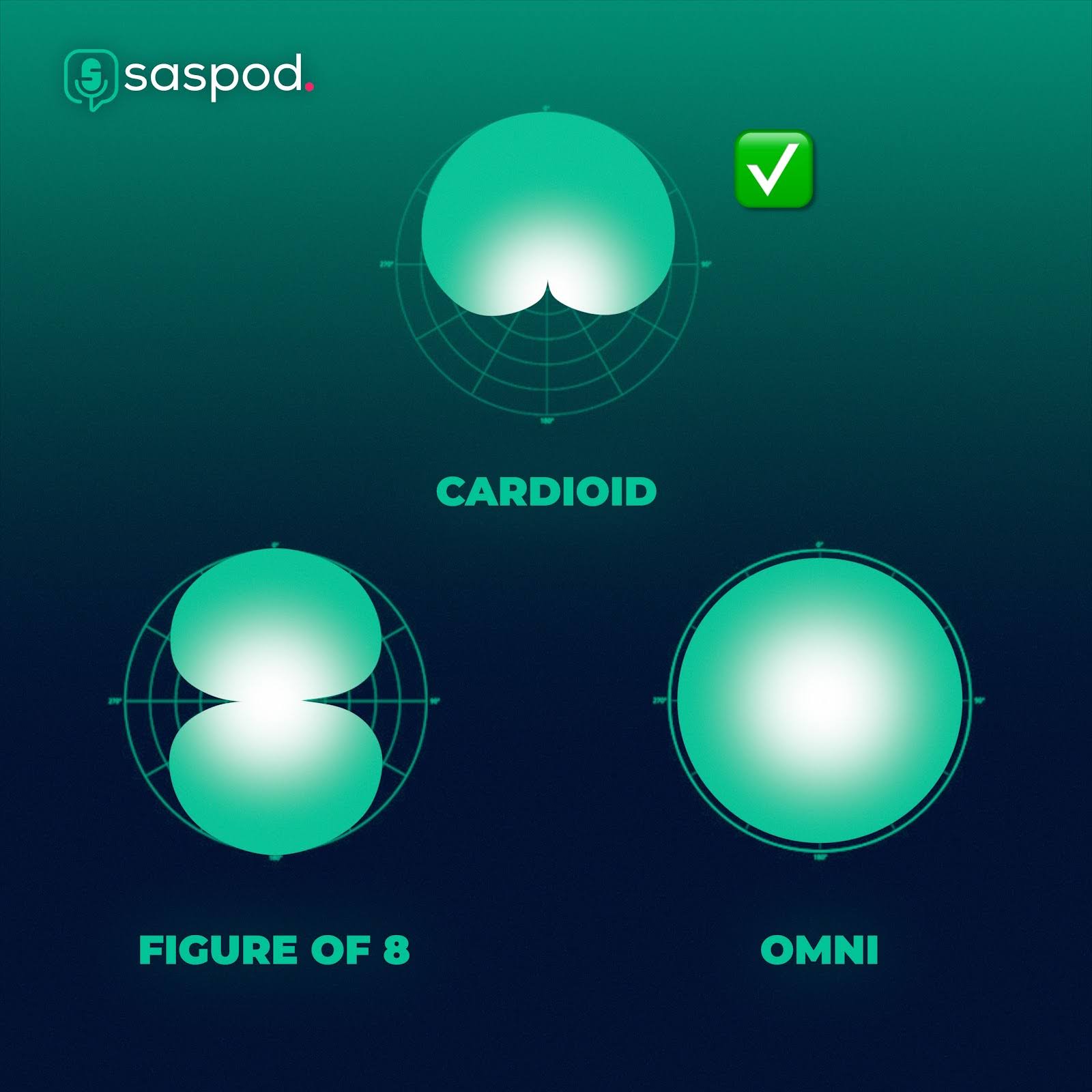
Polar patterns are the recording range of the microphone. Some microphones have a wider recording focus, and some have a narrower focus. A narrower polar pattern is excellent for voice recording in podcasts because it won't pick up any background noise.
Audio Mixer
An audio mixer is an interface that lets you mix the audio channels from your microphones. Using a mixer allows you to set the sound levels and balance the sound before it reaches your DAW. It's a great piece of analog equipment for podcasts, and you can even add a background music channel using an external source.
XLR Microphone
When building your podcast equipment list, you'll probably need an XLR mic. XLR mics plug into your audio mixer before the signal is sent to your PC and DAW. If you're using a condenser or dynamic microphone, you'll need an XLR cable to connect it to your audio mixer.
XLR Cable
XLR cables are an audio engineer's most used tool. XLRs are balanced cables with three wires that connect analog equipment (like microphones and audio mixers.) You'll only need to use XLR cables if you have dynamic or condenser microphones; USB mics plug straight into the PC, so there's no need for the extra cabling.
Pop Filter
Pop filters are small screens that you can attach to your mic stand. They stop hard sounds, like "b" or "p" sounds, from spiking the audio. This useful accessory makes your recording smoother and easier on the ears, and it looks cool.
Podcast Glossary: Audio Recording
Now, we're getting into the technical side of podcasting. Check out our list of podcast words that relate to the technical audio recording aspect of podcasting.
Bit Depth
Some podcast phrases are a bit more technical than others. When you're recording audio, you need to set the bit depth. Bit depth describes the amplitude values that can be recorded for each audio sample. In simple terms, the higher the bit depth, the higher the resolution of audio you'll have. Audio recordings are usually 16-bit, 24-bit, or 32-bit, with 16-bit being lower quality and 32-bit being higher quality.
Bit Rate
Bit rate and bit depth work together in harmony. While bit depth describes the amplitude value range for each audio sample, the bit rate describes how many audio samples per second are captured in the audio waveform. The more snapshots you capture, the higher the sample rate. It's best to record at the highest bit rate possible; typically, 48kHz is used for audio recording.
Clipping
Clipping describes audio distortion that occurs when the signal is too loud. When setting the gain on your input line, you'll need to do a recording test to ensure that the audio won't clip during moments of loudness, like laughing or shouting. Loud noise and clipping damage the audio recording and result in an unpleasant sound, so it's essential to avoid them by running a soundcheck before your podcast starts.
DAW
DAW stands for Digital Audio Workstation. DAWs are the tools used to record, mix, and master the audio files. Popular DAWs include ProTools, Reaper, and Logic Pro.
Gain

Gain is an audio setting that determines the sensitivity of your microphone. If you have a quiet audio source, the gain will be set higher. Similarly, you'll need to pull the gain back if you have a loud audio source. When conducting a sound check, you should take the time to test your audio signal with louder noise and set the gain so the signal stays within the desired audio signal level.
High-Pass Filter
A high-pass filter removes all audio signals that are lower than the determined amount specified. It's a good feature for reducing high-frequency background noise.
Low-Pass Filter
A low-pass filter removes all audio signals lower than the specified amount. It's a good feature for reducing low/rumbling background noise.
Mono
Mono is represented by one audio channel. When recording a single microphone, the audio will be represented by a mono channel.
Stereo
Stereo is represented by two audio channels, left & right. When recording two microphones the first audio channel is panned to the left and the second to the right; the audio will be represented by a stereo channel. Most of the time, music tracks are represented by a stereo channel.
Interface
A podcast audio interface is a piece of audio recording equipment that converts audio signals to a format your computer can recognize. It bypasses the audio mixer and goes straight to your DAW for mixing. Audio interfaces can take analog signals from XLRs and digital signals from jack cables.
Multitrack
Multitrack describes a recording that has multiple audio signals or "tracks." For example, a multitrack podcast recording would involve multiple guests with individual audio tracks.
Hard Limiter / Brickwall Limiter
Audio mixing uses lots of technical software to enhance the audio quality. Hard limiter or Brickwall Limiter describes a technique where a volume limit is set to squash any sound above the set limit. A limited is designed to catch peaks and prevent clipping.
Room Tone
Room tone is the ambient sound of a room when there is no sound. It can be hard to understand, but capturing room tone when podcasting is essential. Record the room tone before you begin so that it can be edited into the background post-production. Room tone will ensure that there are no jarring silences or awkward quiet spots in the recording.
Audio Channels
Audio channels are the different channels of recorded audio on your DAW or audio mixer. Make sure to name each audio channel appropriately to keep track of everything you're recording.
Podcast Glossary: Interviewing
Loads of podcasts base their show around interviewing guests. There are a few podcast words directly related to interviewing that you'll need to know beforehand. Check them out below.
Remote Podcasting
Remote podcasting describes any podcast that is recorded at separate locations. Remote podcasts are captured online over a virtual meeting platform.
Zoom
Zoom is a popular virtual meeting software. It's a great podcast recording software option for podcasters on a budget.
Open-Ended Question
An open-ended question can't be answered with a simple "yes" or "no," it opens the conversation and encourages the guest to share insights and experiences. For example, an open-ended question could be: How would you describe your approach to self-care?
Signature Question
A signature question is a unique question that a podcast host asks every guest. It's a creative way to end the show and can also wrap up an episode by bringing it back to the main theme. Signature questions are always related to the show's theme, and guests are often asked to share their top insights or thoughts on the topic.
Podcast Glossary: Editing
Podcast editing is a trickier aspect of podcasting. Usually, the podcaster will only need to build a podcast equipment list and carry out the recording; the editing is then outsourced to a third party. Learning some of the editing terms is a good idea so you can ask questions and know the correct terms if you have any feedback for your editors.
Waveform
Waveform describes the visual appearance of the audio on the DAW.
Dynamic Effects Processor
Dynamic effects processors are pieces of software that change the dynamic range of audio files. They can reduce or increase the dynamic range to transform the sound.
Compression
Compression is a dynamic effects processor that reduces the dynamic range of audio. It's often used on vocal recordings with varying loudness to level out the sound.
EQ
EQ stands for "Equalizer." An EQ is a dynamic effects processor that lets the audio engineer boost or cut certain frequencies. It's great for cutting background noise and enhancing the point of focus. For example, it could emphasize the podcast host's voice but cut out background fuzz.
Jingle
A jingle is an opening theme song often used in advertising and podcasting. It introduces the show at the start of an episode.
Reverb
Reverb is short for reverberation. Reverb is an audio effect that adds depth to the audio. It's often used in vocal audio to enhance the sound by prolonging it after it is produced.
Post-Production
Post-production refers to all of the editing and mixing processes used after the audio has been recorded. The post-production stage can involve things like autotuning, removing background noise, adding in the room tone, and video editing.
Mixing
Mixing is the process of balancing the audio tracks in a multitrack recording to achieve a clear and balanced sound. Mixing includes editing the audio, adding effects, and using dynamic effects processors.
Mixdown
Mixdown is the complete version of the audio after the mixing process. At this stage, the audio has been mixed and is ready to move to the mastering stage.
Mastering
Mastering is the process of editing the final audio file. Unlike mixing, which involves editing each individual audio track, mastering only involves editing the final combined audio. Software like iZotope's Ozone 11 is extremely popular for completing the mastering process.
Master
The master is the final file form. After the mastering stage is complete, the audio file is called the "Master" version.
Noise Floor
A noisefloor is all of the noise that a recording setup makes without a signal running through it. This noise can include interference, electromagnetic waves, wireless interference, and equipment noise.
Normalization
Normalization is an audio editing technique that adjusts the audio file's overall gain. It adjusts the waveform's perceived loudness to make it bigger or smaller, and it's often used when audio files sound unmatched.
Plug-ins
Plug-ins are additional audio editing tools that you can install on your DAW. Many popular third-party sources create plug-ins for audio editing. There are plenty of reverb, delay, and special effects plug-ins available, some of the most well known companies that create them are Waves, Plugin Alliance, iZotope, just to name a few.
ID3 Tags
An ID3 tag is a type of metadata container used for storing media file information. It stores information like a title, cover art, the year recorded, and more. Using an ID3 tag ensures that the media is displayed correctly on portable media players and software-based audio players.
Stinger/Sting
A podcast stinger (or sting) is a short clip of audio used to introduce the show, end, or link sections together. It's a kind of sound effect that is longer and more complex than a simple air horn sound. A stinger connects "scenes" together or makes transitions between topics feel more natural.
Podcast Glossary: Uploading
Podcast uploading covers everything you need to get your podcast online. You'll need to know some technical podcast words to ensure it's in the correct format for uploading.
Audio encoding
Audio encoding is the process of changing the audio from one format to another. An example is converting the Master audio file from WAV to MP3 files for use on CDs.
Format
Format describes the kind of audio file your project is saved in. Audio formats include MP3 and WAV, but MP4 can also be used for multimedia files like video with audio.
WAV File
A WAV file is a standard audio file format for storing audio bitstream. WAV files are the highest quality audio format, so use this format whenever possible.
Progressive Uploading
Progressive uploading allows you to encode media sources into separate chunks and then upload them to the cloud live during recording. Usually, audio is uploaded separately from the recording after it ends. Using progressive uploading, audio upload and recording can happen simultaneously.
YouTube
YouTube is popular with podcasters. You don't need to have a video podcast to upload your show to YouTube; you can use a static image with your podcast audio to reach YouTube viewers.
SEO
SEO stands for Seach Engine Optimization. SEO helps viewers find your podcast by ranking on search engines. SEO can be used in your episode title, show notes, and timestamps. Choosing the correct category for your podcast is an essential part of SEO, so choose wisely!
RSS Feed
RSS stands for Really Simple Syndication. The RSS feed is a URL link that your hosting site will provide when you upload your podcast files. The RSS feed is updated whenever you publish a new episode or make changes to the podcast.
It contains essential metadata about your podcast, like the title, episode name, contact details, and more. The RSS feed is shared with platforms like Apple Podcasts, so listeners can access it there.
Prefix
A podcast tracking prefix is a URL code that needs to be added to the beginning of a podcast's media URL. The code lets third-party analytic platforms track downloads and user devices without interfering with content distribution. The data helps podcasters gain insights and evaluate marketing effectiveness.
Podcast Glossary: Promotion
Podcast promotion ensures your podcasts teach the ears of your podcast audience. To do this, you'll need to monetize through sponsors and create a marketing plan. Check out our pick of promotion podcast words that we know you'll need to know.
Sponsors
Podcast industry sponsors a podcast to advertise to their audience. It's a great way to monetize a podcast, but make sure to pick sponsors that align with your audience's interests.
Subscribe
When listeners subscribe to your podcast, they'll be notified when new episodes are published. The more subscribers you have, the more loyal listeners will tune in every week. Getting the subscriber count up is an important metric for podcasters.
Analytics
Analytics are metrics used to measure the success of your podcast. Analytics give insight into how effective the marketing of the podcast has been. Some metrics include listenership, clicks and views, geo location, age range, and more.
Attribution
Podcast attribution describes the process of ad impressions and conversions being tracked back to the podcast source. * Define this further
Dynamic Ad Insertion (DAI)
DAI involves inserting ads into a podcast using ad tools. The ad tools allow you to target specific audiences, locations, time of day, and more. The ads aren't read by the hosts but instead are pre-produced and added to podcasts, depending on the target criteria.
Baked-in Ads
Baked-in ads are embedded into the episode's audio file. The host reads the advertisement during the recording, and it becomes a permanent part of the episode. This is the opposite of dynamic ad insertion. Baked-in ads can be easier for smaller podcasting teams to implement and are most useful if you have only a handful of ad sources.
Cost Per Action (CPA)
Cost per action is a transaction agreement where the podcaster is paid per action instead of paid based on listenership. An example of an action could be generating new clients or services purchased for the podcast's sponsor.
Cost Per Download (CPD)
Cost per download is a metric that measures the effectiveness of marketing. It assesses the overall cost required to create podcast downloads.
Cost Per Mille (CPM)
Cost per mile is a metric that measures the cost per thousand listeners or downloads of every ad. For example, if an ad costs $30 CPM, the advertisers will pay $30 per thousand listeners.
Authority
Podcast authority (PA) describes how established your podcast is. The more authority you have within your category, the higher you will rank. Data like downloads, reviews, ratings, and rate of completion of episodes determine PA.
Podcast Visibility Analytics (PVA)
Podcast visibility analytics monitors the visibility of podcasts across different platforms. PVA is a key metric for enabling podcast visibility optimization (PVO.)
Podcast Visibility Optimization (PVO)
Podcast visibility optimization is SEO for podcasting. PVO uses marketing metrics to measure the podcast's reach and how effectively it is distributed to target audiences.
Narrowcast
A narrowcast podcast aims to reach a small target audience as opposed to a wider audience. Broad coasts aim to reach a "broad" audience, while narrowcasts aim to reach a "narrow" audience.
Podcast Glossary: Wrapped Up
Knowing the words to use when podcasting will make your recording and editing process easier, as well as positioning yourself as an expert within the industry. Growing your knowledge and understanding of podcasting is paramount to ensuring the success of your own podcasting podcasts.
If you're looking to start your podcast project, why not begin today? At Saspod, we handle everything from podcast production to hosting and promotion.


Comments
No comments yet!